Page 40 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 40
Shadow
the same thing, as do all gases, including air. Tiny imperfections in a crystal will also scatter light.
The amount of scattering depends on the wavelength (colour) of the light. It is the reason the sky appears blue. Sunlight is scattered as it passes through the air. The blue light is scattered much more than the red light, so that sunlight has less blue than if we saw it from space. That
is why sunlight appears slightly yellow. The blue light continues to be bounced around in the air and eventually reaches the eye. Because it is mostly blue light that is scattered, the sky appears blue.
Skylight
The bluish-coloured light that we see in a clear sky. It is produced by air molecules scattering the sunlight so that more blue light
is scattered in the sky than any other colour. From Earth the Sun looks yellower than it does from space because some of the blue in sunlight has been scattered away into the air.
Space appears black because there are too few particles to scatter the sunlight.
Sonar
(See: Ultrasound.)
Sonic boom
When an aeroplane is moving relatively slowly, there is plenty of time for the air molecules to get out of the way. However, as the aeroplane reaches the speed of sound, it overtakes the moving molecules and compresses the layers of air in its line of flight. At the speed of sound the waves become audible as a sonic boom.
The ratio of the speed of an object to the speed of sound is called the Mach number, after
the Austrian physicist Ernst Mach. Mach 1 is the speed of sound.
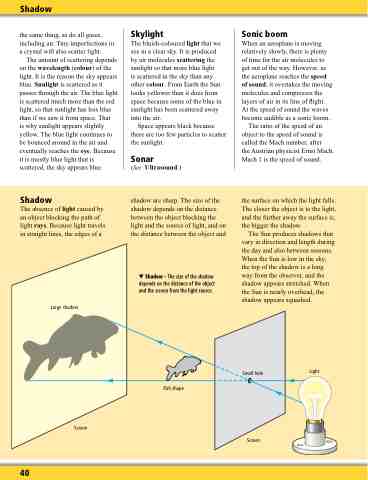
Shadow
The absence of light caused by an object blocking the path of light rays. Because light travels in straight lines, the edges of a
Large shadow
shadow are sharp. The size of the shadow depends on the distance between the object blocking the light and the source of light, and on the distance between the object and
Shadow – The size of the shadow depends on the distance of the object and the screen from the light source.
the surface on which the light falls. The closer the object is to the light, and the further away the surface is, the bigger the shadow.
The Sun produces shadows that vary in direction and length during the day and also between seasons. When the Sun is low in the sky, the top of the shadow is a long way from the observer, and the shadow appears stretched. When the Sun is nearly overhead, the shadow appears squashed.
Small hole
Light
Fish shape
Screen
Screen
40