Page 39 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 39
Scattering of light
where it goes into the water. Once light has passed from one substance to another, it continues in a straight line. The bending only happens at the surface. If light passes from air into a glass block, it will be bent as it enters the glass and again when it leaves. As it leaves the glass, it is bent by the same amount as when it entered, so it leaves in the same direction as it enters, although not in quite the same path. The same thing happens when light passes from air to water in clouds.
The amount by which the light is bent depends on the length of the light waves. Red waves are bent by a different amount than blue waves. If the light passes through
a straight-sided sheet of glass, this difference is removed because the light is bent back when it leaves the glass. However, when light passes through a raindrop or a glass without parallel sides (a prism), it gives rise to a rainbow. (See also: Angle of refraction.) (Compare with: Diffraction of light.)
Refraction of sound
The bending of sound waves as they travel through different kinds of medium. Sound travels faster through warm air than through cool air. During the day the ground
is hotter than the air above. That makes the wave travel in a curve upwards, quickly taking the sound out of hearing. At night the situation is reversed and the sound is deflected downwards, allowing people to hear more clearly and for greater distances than by day. (See also: Diffraction of sound.)
Resolving power
The ability to tell closely spaced objects apart. It is related to the size of the main, or objective, lens in a telescope. The bigger the objective lens, the better the resolving power.
Retina
The inner surface of the back of the eye. It is covered in light-sensitive cells in the shape of cones and rods.
Reverberation
The sounds reflected from walls and ceilings that reach the listener fractionally after the direct sound. If the time delay between the direct sound and the reflected sounds is more than 0.05 seconds, the sounds can be heard distinctly and are called echoes.
Reverberation is strong in places like churches and much organ music relies on reverberation from the walls for its effect.
Reverberation accounts for the time a sound takes to decay (fade away). It is part of the acoustics of a room.
S
Saturation
The property of a colour that determines how vivid it looks. It compares the colour to a grey at the same level of brightness.
Scattering of light
When light passes through a substance, some of it is soaked
up (see: Absorption of light),
but much more is bounced off
in all directions (see: Reflection). Imagine light passing through a cloud containing billions of tiny water droplets. Light hits a droplet and a tiny amount of light goes straight through. Most bounces off the surface of the drop and heads off in a new direction. Smoke does
39
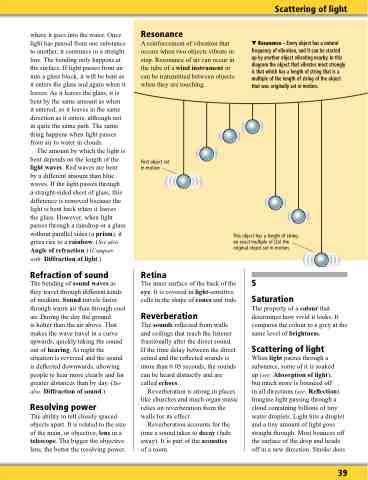
Resonance
A reinforcement of vibration that occurs when two objects vibrate in step. Resonance of air can occur in the tube of a wind instrument or can be transmitted between objects when they are touching.
First object set in motion
Resonance – Every object has a natural frequency of vibration, and it can be started up by another object vibrating nearby. In this diagram the object that vibrates most strongly is that which has a length of string that is a multiple of the length of string of the object that was originally set in motion.
This object has a length of string an exact multiple of (2x) the original object set in motion.