Page 28 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book
P. 28
Lead in batteries
One of the biggest users of lead and lead oxide is the storage battery industry. The main plates used in lead-acid batteries are made from grids of lead alloy, alternate plates being coated with “spongy” lead and lead oxide.
The lead-acid battery is made of a number of units,
each called cells. Every cell in a lead-acid battery can generate approximately 2 volts of electricity. In a car battery, six cells are placed in series, producing a total of about 12 volts.
Bubbles of gas seen during charging are due to the splitting of some water molecules into oxygen and hydrogen gases.
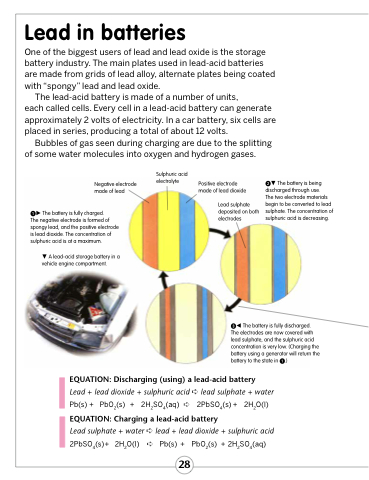
Negative electrode made of lead
The battery is fully charged.
The negative electrode is formed of spongy lead, and the positive electrode is lead dioxide. The concentration of sulphuric acid is at a maximum.
A lead-acid storage battery in a vehicle engine compartment.
Sulphuric acid electrolyte
Positive electrode made of lead dioxide
Lead sulphate deposited on both electrodes
The battery is being discharged through use.
The two electrode materials begin to be converted to lead sulphate. The concentration of sulphuric acid is decreasing.
EQUATION: Discharging (using) a lead-acid battery
Lead + lead dioxide + sulphuric acid ➪ lead sulphate + water Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq) ➪ 2PbSO4(s) + 2H2O(l)
EQUATION: Charging a lead-acid battery
Lead sulphate + water ➪ lead + lead dioxide + sulphuric acid 2PbSO4(s)+ 2H2O(l) ➪ Pb(s) + PbO2(s) + 2H2SO4(aq)
The battery is fully discharged. The electrodes are now covered with lead sulphate, and the sulphuric acid concentration is very low. (Charging the battery using a generator will return the battery to the state in .)
28