Page 18 - Curriculum Visions Dynamic Book. To close the book, close the tab.
P. 18
Frequency
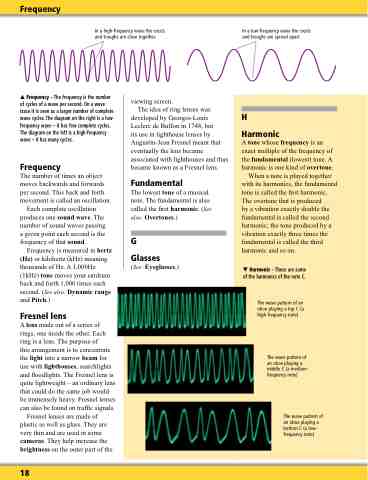
In a high-frequency wave the crests and troughs are close together.
In a low-frequency wave the crests and troughs are spread apart.
Frequency – The frequency is the number of cycles of a wave per second. On a wave trace it is seen as a larger number of complete wave cycles. The diagram on the right is a low- frequency wave – it has few complete cycles. The diagram on the left is a high-frequency wave – it has many cycles.
Frequency
The number of times an object moves backwards and forwards per second. This back and forth movement is called an oscillation.
Each complete oscillation produces one sound wave. The number of sound waves passing a given point each second is the frequency of that sound.
Frequency is measured in hertz (Hz) or kilohertz (kHz) meaning thousands of Hz. A 1,000Hz (1kHz) tone moves your eardrum back and forth 1,000 times each second. (See also: Dynamic range and Pitch.)
Fresnel lens
A lens made out of a series of rings, one inside the other. Each ring is a lens. The purpose of
this arrangement is to concentrate the light into a narrow beam for use with lighthouses, searchlights and floodlights. The Fresnel lens is quite lightweight – an ordinary lens that could do the same job would be immensely heavy. Fresnel lenses can also be found on traffic signals.
Fresnel lenses are made of plastic as well as glass. They are very thin and are used in some cameras. They help increase the brightness on the outer part of the
viewing screen.
The idea of ring lenses was
developed by Georges-Louis Leclerc de Buffon in 1748, but
its use in lighthouse lenses by Augustin-Jean Fresnel meant that eventually the lens became associated with lighthouses and thus became known as a Fresnel lens.
Fundamental
The lowest tone of a musical note. The fundamental is also called the first harmonic. (See also: Overtones.)
G
Glasses
(See: Eyeglasses.)
18
H
Harmonic
A tone whose frequency is an exact multiple of the frequency of the fundamental (lowest) tone. A harmonic is one kind of overtone.
When a note is played together with its harmonics, the fundamental tone is called the first harmonic. The overtone that is produced
by a vibration exactly double the fundamental is called the second harmonic; the tone produced by a vibration exactly three times the fundamental is called the third harmonic and so on.
Harmonic – These are some of the harmonics of the note C.
The wave pattern of an oboe playing a top C (a high-frequency note)
The wave pattern of an oboe playing a middle C (a medium- frequency note)
The wave pattern of an oboe playing a bottom C (a low- frequency note)